FAQ
When should I enable static IP for Prisma Accelerate?
Enable static IP for Accelerate when your security setup requires IP allowlisting or if you're implementing firewalls that only permit access from trusted IPs, ensuring controlled and secure database connections.
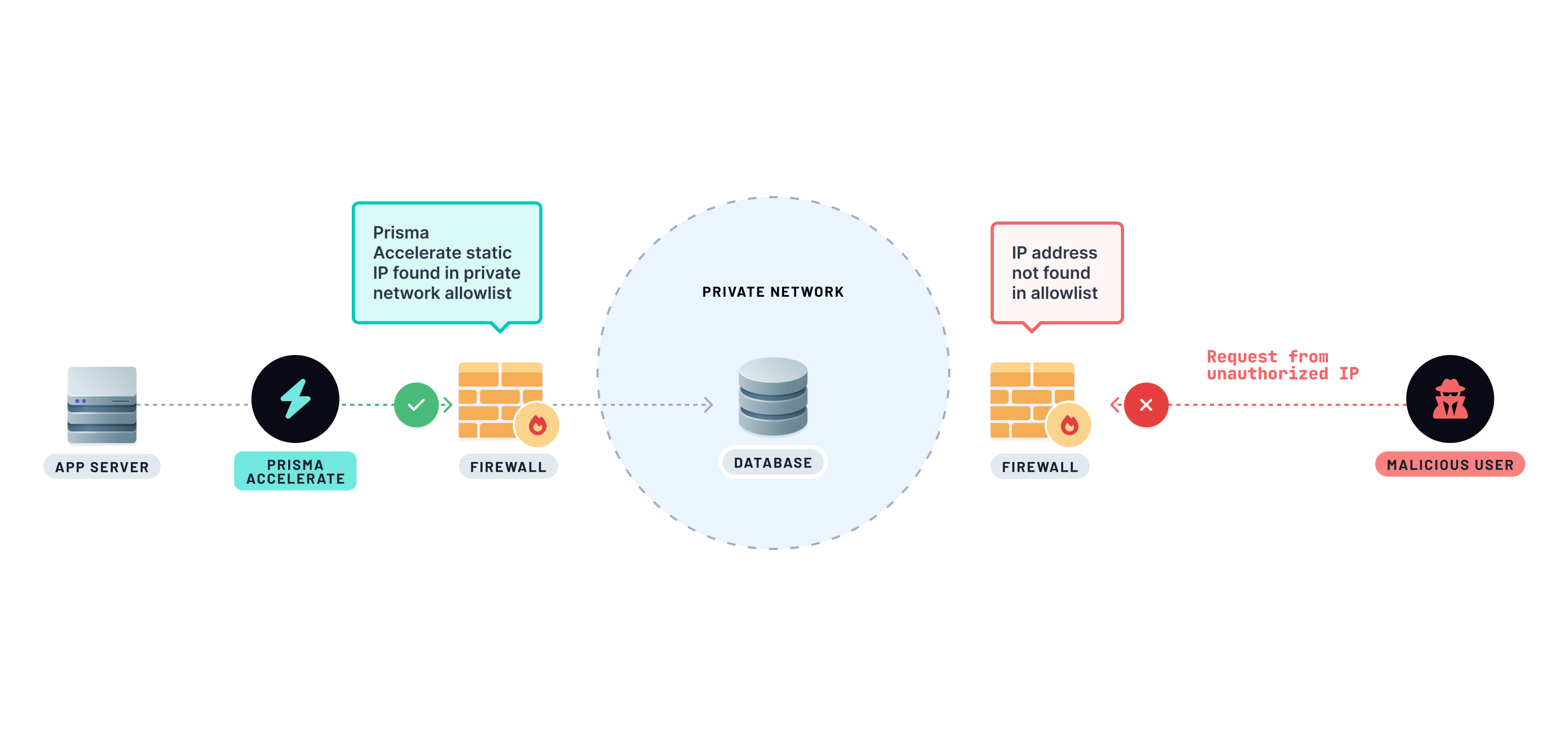
Learn more on how to enable static IP for Accelerate in the Platform Console.
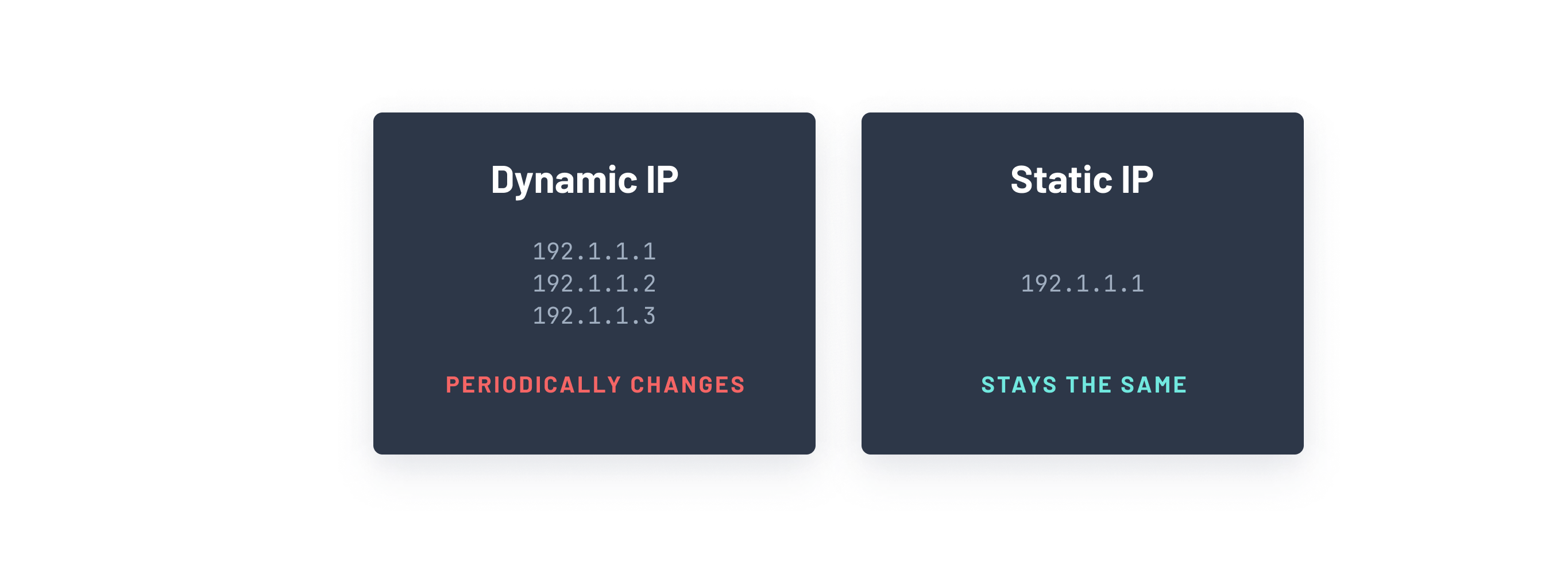
What is a static IP?
A static IP address is an IPv4 or an IPv6 address that is fixed. Unlike dynamic IP addresses, which can change unpredictably, traffic from static IP addresses can be easily identified.
ℹ️ To enable static IP support for Accelerate within your existing or new project environment, your workspace will need to be on our Pro or Business plans. Take a look at the pricing page for more information.
Why do I sometimes see unexpected cache behavior?
Accelerate's cache performs best when it observes a higher load from a project. Many cache operations, such as committing data to cache and refreshing stale data, happen asynchronously. When benchmarking Accelerate, we recommend doing so with loops or a load testing approach. This will mimic higher load scenarios better and reduce outliers from low frequency operations.
Prisma operations are sent to Accelerate over HTTP. As a result, the first request to Accelerate must establish an HTTP handshake and may have additional latency as a result. We're exploring ways to reduce this initial request latency in the future.
What is the pricing of Accelerate?
You can find more details on our Accelerate pricing page
VS Code does not recognize the $extends method
If you add the Prisma Client extension for Accelerate to an existing project that is currently open in VS Code, the editor might not immediately recognize the $extends method.
This might be an issue with the TypeScript server not yet recognizing the regenerated Prisma Client. To resolve this, you need to restart TypeScript.
- In VS Code, open the Command Palette. You can do so when you press F1 or select View > Command Palette.
- Enter
typescriptand select and run the TypeScript: Restart TS server command.
VS Code should now recognize the $extends method.
What regions are Accelerate's cache nodes available in?
Accelerate runs on Cloudflare's network and cache hits are served from Cloudflare's 300+ locations. You can find the regions where Accelerate's cache nodes are available here: https://www.cloudflare.com/network/.
What regions is Accelerate's connection pool available in?
When no cache strategy is specified or in the event of a cache miss, the Prisma Client query is routed through Accelerate's connection pool. Currently, queries can be routed through any chosen region among the 16 available locations.
Currently, the list of available regions are:
- Asia Pacific, Mumbai (
ap-south-1) - Asia Pacific, Seoul (
ap-northeast-2) - Asia Pacific, Singapore (
ap-southeast-1) - Asia Pacific, Sydney (
ap-southeast-2) - Asia Pacific, Tokyo (
ap-northeast-1) - Canada, Central (
ca-central-1) - Europe, Frankfurt (
eu-central-1) - Europe, Ireland (
eu-west-1) - Europe, London (
eu-west-2) - Europe, Paris (
eu-west-3) - Europe, Stockholm (
eu-north-1) - South America, Sao Paulo (
sa-east-1) - US East, N. Virginia (
us-east-1) - US East, Ohio (
us-east-2) - US West, N. California (
us-west-1) - US West, Oregon (
us-west-2)
You can also view the available regions when you're about to set up Accelerate or by visiting the Settings tab for Accelerate under the Region section in the Prisma Cloud Platform dashboard.
How does Accelerate know what region to fetch the cache from?
Under the hood, Accelerate uses Cloudflare, which uses Anycast for network addressing and routing. An incoming request will be routed to the nearest data center or "node" in their network that has the capacity to process the request efficiently. To learn more about how this works, we recommend looking into Anycast.
How can I invalidate a cache on Accelerate?
You can invalidate the cache on-demand via the $accelerate.invalidate API if you're on a paid plan, or you can invalidate your entire cache, on a project level, a maximum of five times a day. This limit is set based on your plan. You can manage this via the Accelerate configuration page.
What is Accelerate's consistency model?
Accelerate does not have a consistency model. It is not a distributed system where nodes need to reach a consensus (because data is only stored in the cache node(s) closest to the user). However, the data cached in Accelerate's cache nodes doesn't propagate to other nodes, so Accelerate by design doesn't need a consistency model.
Accelerate implements a read-through caching strategy particularly suitable for read-heavy workloads.
The freshness of the data served by the cache depends on the cache strategy defined in your query. Refer to this section for more information on selecting the right cache strategy for your query.
How is Accelerate different from other caching tools, such as Redis?
- Accelerate is a specialized cache that allows you to optimize data access in code at the query level with a cache strategy. On the other hand, tools such as Redis and Memcached are general-purpose caches designed to be adaptable and flexible.
- Accelerate is a managed service that reduces the time, risk, and engineering effort of building and maintaining a cache service.
- By default, Accelerate is globally distributed, reducing the latency of your queries. Other cache tools would require additional configuration to make them available globally.
When should I not use Accelerate's caching features?
Accelerate is a global data cache and connection pool that allows you to optimize data access in code at the query level. While caching with Accelerate can greatly boost the performance of your app, it may not always the best choice for your use case.
Accelerate's global cache feature may not be a good fit for your app if:
-
Your app is exclusively used within a specific region and both your application server and database are situated in that same region on the same network. For example, database queries will likely be much faster if your application server and database are in the same region and network. However, If your application server is in different regions or networks from your database, Accelerate will speed up your queries because the data will be cached in the closest data center to your application.
-
You only need a general-purpose cache. Accelerate is a connection pooler and a specialized cache that only caches your database query responses in code. A general-purpose cache, such as Redis, would allow you to cache data from multiple sources, such as external APIs, which Accelerate currently doesn't support. If general-purpose caching interests you, please share your feedback with us via our Discord.
-
Your application data always needs to be up-to-date on retrieval, making it difficult to establish a reasonable cache strategy.
Even without using Accelerate's global cache, you can still greatly benefit from Accelerate by using its connection pool, especially in serverless or edge functions, where it is difficult to manage and scale database connections. You can learn more about the serverless challenge here.
Can I use Accelerate with other ORMs/query builders/drivers?
No. We currently do not have any plans for supporting other ORMs/query builders or drivers. However, if you're interested in support for other libraries, feel free to reach out and let us know in our Discord community in the #help-and-questions channel.
What is the maximum allowed value for the ttl parameter when configuring cacheStrategy?
The Time-to-live (ttl) parameter can be set for up to a year. However, it's important to note that items within the cache may be evicted if they are not frequently accessed.
Based on our experimentation, we’ve seen cache items persist for around 18 hours. While items may remain in the cache for an extended period if they are actively accessed, there is no guarantee.
Note: Even frequently accessed items may occasionally be evicted from the cache. It's unlikely for an item to survive for up to or longer than a month, regardless of its activity level.
Why doesn’t Accelerate fall back to the direct connection string during a service disruption?
In the rare event of a service disruption, falling back to a direct connection would bypass the connection pool. This could potentially deplete the database's available connections and cause other issues on the database level.
If there is a service disruption, it's recommended to verify on the status page. You can reach out to one of Prisma's support channels for assistance.
Note: Additionally, it's worth noting that some edge function runtime environments may not support direct connections with Prisma ORM. For further details, refer to our Edge functions documentation.
Are each of the queries within an interactive transaction counted separately for billing?
Yes, interactive transactions are billed based on the individual operations within the transaction. There is no charge for the start, commit, or rollback of the transaction itself. For example, in the following query, there are two billable queries:
await prisma.$transaction(async (tx) => {
await tx.user.deleteMany({ where: { name: 'John Doe' } });
await tx.user.createMany({ data });
});
However, when using the $transaction API for sequential client operations, regardless of the number of queries within the array, it counts as only one billable query. For example:
await prisma.$transaction([
prisma.user.deleteMany({ where: { name: 'John Doe' } }),
prisma.user.createMany({ data }),
]);
If you don't need interactive transactions, you can save costs and improve performance by using sequential operations transactions. Sequential operations transactions perform better on Accelerate because they execute in one round-trip to the database, while interactive transactions require separate round-trips for start, commit, and each individual operation on the transaction.
Can I increase my Accelerate query duration and response size limits?
Yes, you can increase your Accelerate limits based on your subscription plan. Here are the configurable limits:
| Limit | Starter | Pro Plan | Business Plan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query timeout | Up to 10 seconds | Up to 20 seconds | Up to 60 seconds |
| Interactive transactions timeout | Up to 15 seconds | Up to 30 seconds | Up to 90 seconds |
| Response size | Up to 5 MB | Up to 10 MB | Up to 20 MB |
Check the pricing page for more details on the available plans and their corresponding limits.
While you can increase these limits based on your subscription plan, it's still recommended to optimize your database operations. Learn more in our troubleshooting guide.
How long does it take to invalidate a cache query result?
As the cache needs to be cleared globally, it is difficult to provide a specific time frame. However, the cached data is eventually consistent and typically propagates to all PoPs within a few seconds. In very rare cases, it may take longer.
Here is a demo app to test the time it takes to invalidate a cache query result.
What is the difference between Invalidate and Revalidate?
Invalidate: The cache entry is deleted, and new data will be fetched on the next request, causing a cache miss. This removes stale data but may lead to slower responses until the cache is repopulated.
Revalidate: The cache entry is updated proactively, ensuring the next request uses fresh data from the cache. This keeps the cache valid and maintains faster response times by avoiding cache misses.
What is on-demand cache invalidation?
On-demand cache invalidation lets applications instantly update specific cached data when it changes, instead of waiting for regular cache refresh cycles. This keeps information accurate and up-to-date for users.
When should I use the cache invalidate API?
The cache invalidate API is essential when data consistency cannot wait for the cache’s standard expiration or revalidation. Key use cases include:
- Content updates: When critical changes occur, such as edits to a published article, product updates, or profile modifications, that need to be visible immediately.
- Inventory management: In real-time applications, like inventory or booking systems, where stock levels, availability, or reservation statuses must reflect the latest information.
- High-priority data: For time-sensitive data, like breaking news or urgent notifications, where it’s essential for users to see the most current information right away.
Using on-demand cache invalidation in these scenarios helps keep only the necessary data refreshed, preserving system performance while ensuring accurate, up-to-date information for users.
How does Accelerate count queries for billing?
Accelerate counts queries at the Prisma Client invocation level. A single Prisma query may translate into multiple SQL statements under the hood, but it will only count as one query for billing purposes. This ensures straightforward, predictable billing that reflects the Prisma Client usage rather than the complexity of the underlying SQL operations.
Queries are counted regardless of whether they are served from the cache or the database. Even if a query is retrieved from the cache, it still counts toward your query limit.
How do I switch from GitHub login to email and password login?
If you previously signed up using GitHub and want to switch to email and password login, follow these steps:
1. Verify Your GitHub Email Address
- Check the primary email address associated with your GitHub account (e.g., from your GitHub profile or notification settings).
2. Create a New Email/Password Account
- Go to the email/password sign-up page.
- Use the same email address linked to your GitHub account to create the new account.
- Our system will automatically connect your new email/password account to your existing data.
3. Test Your Login
- Log out and try logging in with your email and the password you just created.
Note: If you encounter any issues, please contact our support team for help linking your accounts.